This is an informative post about MR16.

MR16 is a standard specification for halogen reflector lamps established by various manufacturers. Nowadays, LED lamps in the MR16 form factor can also be found.
Applications:
MR16 lamps are commonly used to replace compact fluorescent lamps or standard incandescent light bulbs in applications such as residential lighting and retail lighting. MR16 lamps were originally designed for slide projectors but are now suitable for various applications requiring directional lighting from low to medium intensity. These applications include track lighting, recessed ceiling lights, desk lamps, pendant lights, fixtures, landscape lighting, retail display lighting, and bicycle headlights.
Performance:
MR16 is a designation where "MR" stands for Multifaceted Reflector, and "16" represents the length of the front diameter as a multiple of units, where 8 units equal 1 inch. For example, in the case of MR16, the front diameter is 16 units long, which corresponds to 2 inches or approximately 5.08 cm in diameter.
So MR16 is one type of MR lamp series. MR lamps are composed of a light source (halogen or other bulbs), a multifaceted reflector, and a base that complies with the GU5.3 double-pin standard. The reflector can control the direction and range of the projected light, and different MR lamps have different beam angles. Narrow spotlights can be as small as 7°, while wide floodlights can be as large as 60°.
Performance Parameters:
Here are brief introductions to some performance parameters of MR16 LED drivers:
① ZXLD1320 (Buck-Type): Input Voltage Range: DC 4V-18V, Maximum Output Current: 1.5A, Efficiency: >85%, Supports DC/PWM dimming, Soft start, Thermal control, Over-temperature protection, Supports up to 4 LEDs in series.
② ZXLD1321 (Boost-Type): Input Voltage Range: DC 1V-12V, Maximum Output Current: 1A, Efficiency: >85%, Supports DC/PWM dimming, Soft start, Thermal control, Over-temperature protection, Supports up to 5 LEDs in series.
③ ZXLD1322 (Buck-Boost Type): Input Voltage Range: DC 2.5V-15V, Maximum Output Current: 700mA.
These MR16 LED driver options offer various voltage input ranges, output current capabilities, and features like dimming, soft start, thermal control, and over-temperature protection to suit different lighting applications.
The MR16 lamp was first introduced to the market in 1965. In 1967, Emmett H. Wiley from General Electric in the United States made modifications to these lamps, resulting in a patented micro-reflector lamp. His innovation primarily focused on using the lamp's edge, rather than the lamp's base, as the reference plane for focusing. This change made the installation of these lamps more flexible and improved the precision of focusing. However, at that time, the reflectors used in these lamps were not yet "multifaceted," and multifaceted reflectors were introduced around 1971.
Thanks to the outstanding color rendering and beam angle control of MR16 lamps, they became hugely popular worldwide and established a dominant position in the lighting industry at the time. This position was only broken after 2000. With the development of the economy and technology, LED technology began to proliferate, leading to the introduction of numerous new lighting fixtures. As a new generation of lighting emerged, traditional lighting was gradually overshadowed by modern lighting, marking the end of an era.
The design of MR16 LED drivers presents several challenges, primarily in the following areas:
Constant Current Accuracy: One of the key challenges in MR16 LED driver design is achieving precise constant current regulation. Currently, there are two main categories of control chips used for MR16 LEDs: PWM control and hysteretic control. PWM control, employed by chips like ACT111, PT4105, AMC7150, NCP3065, offers higher current regulation accuracy but can be more complex in circuit structure with more components. The choice between these control methods should consider the available space in the MR16 base.
Conversion Efficiency: The conversion efficiency of LED drivers is closely related to factors such as the control chip's switching frequency, the on-resistance of internal switches, and the DC resistance (DCR) of the freewheeling inductor. LED drivers with NPN switches are generally not suitable for MR16 LED drivers, especially as the output power requirements increase. NPN switches can result in higher power losses and hinder efficiency improvements. Lower-frequency operation also necessitates larger inductance and filtering capacitance values, which can impact efficiency and create PCB layout challenges.
Cost Considerations: The cost of MR16 LED drivers is a significant consideration. During the initial market introduction, these products may have higher profit margins. However, as they enter regular production, profit margins can decrease significantly. Given that MR16 LED drivers typically operate at AC12V or DC12V input voltages, the choice of control chip should consider a narrow working voltage range to keep costs in check. Broader working voltage ranges in control chips tend to increase costs and can represent a significant portion of the overall driver cost.
Balancing these challenges is crucial in designing efficient, cost-effective MR16 LED drivers that meet the required constant current accuracy while optimizing conversion efficiency within the constraints of size and cost considerations.
Compared to modern lighting fixtures, traditional lamps have several significant drawbacks. Two major issues are the high temperatures generated when the lamp is on and the risk of the pressurized bulb exploding. For example, halogen bulbs can reach temperatures above 200°C when lit. If any flammable material comes into contact with or even gets close to the bulb or its base, it can potentially lead to a fire accident. Similarly, quartz bulbs containing tungsten filaments and halogen gas are pressurized. If mishandled or damaged, they can explode. These drawbacks have strong life-threatening implications, making their elimination from society only a matter of time.
MR16 did experience a period of silence during this lighting revolution. However, true champions refuse to concede defeat. Soon, with the rapid development of new LED technology, MR16 underwent an upgrade, giving birth to the LED version of MR16 and breathing new life into the MR16 lighting category.
The LED version of MR16 largely retains the original design but replaces the traditional light source with LED technology. Additionally, the multifaceted reflector's housing cleverly transforms into a heat sink.
LED MR lamp housing radiator

Comparison chart between traditional light source and LED light source MR16
The LED version of MR16 addresses issues such as power consumption, heat generation, and the risk of explosions. Even when providing the same brightness, LED lights emit much less heat and consume significantly less electricity compared to traditional light sources.
The technological advancements in MR16 have been swift. LEDER Lighting Manufacturer, for instance, offers an MR16 series with technology capable of achieving Ra97, 7.5W, and 600 lumens. Importantly, the LEDER MR16 can precisely control the beam angle, including options like 8 degrees, 15 degrees, 24 degrees, 36 degrees, and 60 degrees. Among these, the 8-degree MR16 boasts a center beam intensity exceeding 5500cd.
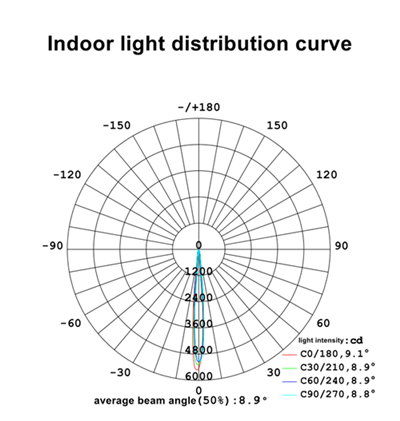
LEDER MR16 8° light distribution curve
MR16 can be adapted to various casings, with different styles chosen based on the opening size and aesthetic requirements of the environment.

MR16 frameless case

MR16 shell

MR16 thin case
Compared to traditional halogen lamps, current technology allows for dimming, high lumen output, better efficiency, and longer lifespan. These advancements will undoubtedly contribute to MR16 regaining its prominent position in the lighting industry.
Contact: Mr. Otis
Phone: +8615815758133
Tel: +8615815758133
Email: Hello@lederlighting.com
Add: No. 1 Gaoxin West Road,High-tech Zone, Jiangmen, Guangdong, China