
LED street lights utilize various lighting arrangements tailored to the specific characteristics of different roads and locations. Conventional lighting fixtures typically employ five fundamental layouts: single-sided, double-sided staggered, bilateral symmetrical, central symmetrical, and transverse suspension layouts, as illustrated in Figure 7-1. The choice of layout depends on factors such as the road's cross-sectional shape, width, and lighting requirements.
For instance:
(a) Single side arrangement
(b) Staggered arrangement on both sides
(c) Bilateral symmetrical arrangement
(d) Centrally symmetrical arrangement
(e) Transverse suspension cable arrangement
Determining the spacing between street lights involves considerations such as lighting layouts, types of light distribution, and installation heights, detailed in Table 7-1. The optimal arrangement should be selected based on the specific characteristics of the road, ensuring efficient and adequate lighting coverage.
Figure 7-1 Common road lighting arrangements
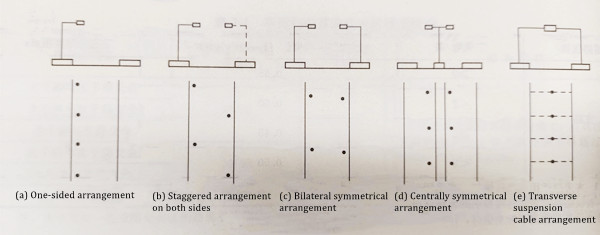
Table 7-7 Street light spacing corresponding to different layout methods, light distribution types, and installation heights | ||||||
Light distribution type | Cutoff type | half light type | Non-cutting type | |||
Arrangement | Installation height H/m | Spacing S/m | Installation height H/m | Spacing S/m | Installation height H/m | Spacing S/m |
Single side arrangement | H≥1.0W | S≤3H | H≥1.2W | S≤3.5H | H≥1.4W | S≤4H |
Staggered arrangement on both sides | H≥0.7W | S≤3H | H≥0.8W | S≤3.5H | H≥0.5W | S≤4H |
Symmetrical arrangement on both sides | H≥0.5W | S≤3H | H≥0.6W | S≤3.5H | H≥0.7W | S≤4H |
When assessing LED street lights, prioritizing safety considerations is paramount. Alongside conventional criteria like voltage endurance, insulation resistance, grounding, electric shock protection, heat resistance, flame resistance, leakage resistance, and electromagnetic compatibility, LED street lights demand a focus on specific factors due to their unique application contexts. Dust protection, waterproofing, lightning resistance, wind pressure resilience, and climate adaptation become crucial aspects requiring evaluation.
Given LED light sources' sensitivity to heat, thermal testing, particularly temperature rise assessments of key components, assumes significance. While existing standards apply to LED street lights, they often overlook the fundamental differences between LED and traditional street lighting systems.
In road lighting, variations in road surface areas and lamp pole heights necessitate distinct spatial light distribution requirements for street lights. Consequently, the performance and testing of light distribution in these lights hold significant importance. Photometric measurement standards tailored for lamps exist within the industry to address these specific needs.
(1) Scope of Application:
This specification pertains to outdoor LED road lighting fixtures, encompassing power supplies, heat dissipation devices, optical designs, and associated mechanical structures.
(2) Measurement Conditions:
A. Temperature: In absence of specific provisions, measurements are conducted at an ambient temperature of 25°C ± 2°C, achieving thermal equilibrium through natural convection without direct air supply to the tested LED street light.
B. Humidity: Unless specified otherwise, the relative humidity is maintained at 60% ± 20%.
C. Stability: The LED lighting fixture being tested remains illuminated from the lamp body, ensuring stability for a minimum of 60 minutes before measurement.
D. Testing Power Supply: The test operates within a power supply voltage variation range of ±0.5% and a power supply frequency variation range of ±0.5%.
E. Considerations for Luminous Intensity or Luminous Flux Measurement:
a. The measuring distance exceeds ten times the size of the LED lighting fixture.
b. The darkroom background illumination on the sample test bench does not exceed 0.05 lx.
c. The light intensity meter’s energy range must cover at least 1 to 5000cd.
d. The resolution of the light intensity meter is equal to or less than 0.1%.
e. The accuracy of the light intensity meter's visual effect function is equal to or less than 3%.
These specifications outline the specific conditions and parameters necessary for accurately measuring and evaluating LED street lights for outdoor applications.
(3) Specifications:
① Insulation Resistance: As per the test method, the insulation resistance should measure above 5MA.
② Insulation Voltage Withstand: Subject to a method test, the fixture must endure applied voltage for 1 minute, with a leakage current below 10mA and no abnormalities.
③ Lamp Activation: Following a method test, the luminous flux after drying and lighting should be at least 97% (inclusive) of the initial luminous flux before lighting.
④Basic Characteristics: As per the method test:
* LED street lamp power factor must exceed 0.9, with the power factor test value exceeding 95% of the labeled value.
* The total circuit power must fall within the manufacturer's labeled value of ±110%.
* Harmonic distortion of the input current must not exceed the value specified in Table 7-8.
* The total harmonic distortion of the current should not surpass 33%.
LED light source color temperature classification is detailed in Table 7-9.
Table 7-8 Harmonic allowable values
Harmonic allowable value | |
Harmonic order/order | Maximum allowable harmonics |
200% | 2% |
300% | 30%X |
500% | 10% |
700% | 7% |
900% | 5% |
11≤X≤39 | 3% |
Table 7-9 Color temperature segmentation
Color temperature segmentation | |
Normal CCT | CCT |
2700 | 2725±145 |
3000 | 3045±175 |
3500 | 3465±245 |
4000 | 3985±275 |
4500 | 4503±243 |
5000 | 5028±283 |
5700 | 5665±355 |
6500 | 6530±510 |
⑤ Light Distribution Characteristics: According to the method test, the luminosity distribution of LED lamps must align with the specifications outlined in Table 7-10 (refer to Figure 7-2). Additionally, the initial luminous efficiency of LED street lamps should not fall below the minimum thresholds specified in Table 7-11.
Table 7-10 Light distribution characteristics of lamps Luminous intensity (cd) / Luminous flux of lamps (klm)
Lamp form | vertical angle 90° | vertical angle 80° | vertical angle 70° | vertical angle 65° | vertical angle 60° | |
horizontal angle 95° | horizontal angle 90° | horizontal angle 65~95° | horizontal angle 65~95° | horizontal angle 65~95° | ||
Two directions (type) | Screen type | Below 10 | Below 30 | —— | —— |
|
Semi-shielded type A | Below 30 | Below 120 | —— | More than 90 | —— | |
Semi-shielded type B | Below 60 | Below 150 | —— | More than 150 | —— | |
Unshielded type | Below 100 | —— | More than 150 | —— | —— | |
Full circle (type) | Screen type | Below 10 | Below 30 | —— | —— | —— |
Semi-shielded type | Below 60 | Below 150 | —— | —— | —— | |
Unshielded type | —— | —— | —— | —— | —— | |
Table 7-11 Initial luminous efficiency of lamps
Grade | Luminous efficiency/(lm/W) |
1 | 75 |
2 | 60 |
3 | 50 |
⑥ Voltage Change Rate:
In the method test, LED street lights should operate within ±10% of the rated input voltage range under AC power. Additionally, the center luminous intensity drift must remain within ±5%.
⑦ Temperature Cycle:
As per the method test, LED street lights must function normally within an ambient temperature range of -5°C to 50°C. All components should remain intact without cracks or physical damage, and no LED should fail during operation.
⑧ Switch Test:
In the method test, LED street lights should endure a minimum of 1,200 switching cycles under normal working conditions without any subsequent failures.
⑨ Durability Test:
Following temperature cycles, switching tests, and durability assessments, LED street lights must operate normally at an ambient temperature of 60°C±2°C. All components should remain undamaged, and the luminous flux should not decrease below 90% of the original flux.
⑩ Temperature-Resistant Switch:
During the method test, LED street lights should operate flawlessly at a temperature of 40°C ± 2°C and a relative humidity of 90%~98%RH. All components should remain intact without any damage, and no LED should exhibit failure.
⑪ Surge Protection:
For compliance, LED street lights must incorporate voltage surge protection and meet the requirements outlined in CNS 14676-5 "Electromagnetic Compatibility Testing and Measurement Technology Part 5: Surge Immunity Test". They should continue to operate normally post-test.
⑫ Electromagnetism:
Conforming to CNS 14115 regulations, LED street lights must pass the prescribed method test.
⑬ Dustproof and Waterproofing:
As per method testing aligned with CNS 14165 IP65 regulations, LED street lights must demonstrate compliance. If the power supply is external, it should meet IP54 requirements.
⑭ Wind Tunnel Test:
In the method test, LED street lights must remain intact without deformation, loosening, falling off, or cracking under specified conditions.
(4) Test Method:
①Insulation Resistance Test:
Collect all live parts between non-charged metals (if the shell material is synthetic resin, cover it with conductive metal).
Employ a DC 500V insulation resistance meter to measure insulation resistance between the two terminals and non-charged metal.
②Insulation Withstand Voltage Test:
Conducted subsequent to the insulation resistance test.
Apply a test voltage of 1500V to the live parts and non-charged metal parts, enduring the applied voltage for 1 minute without exhibiting abnormalities.
③Lamp Activation Test:
Illuminate the LED street light by applying rated voltage and input frequency between the input terminals.
Maintain continuous illumination for 1000 hours under indoor, wind-free conditions.
After drying and lighting, measure the lamp's luminous flux based on the defined light distribution curve, defining the lamp's initial luminous flux.
④Basic Characteristics Test:
Apply the rated voltage and input frequency between the input terminals after the LED street lamp has operated for 1000 hours.
After stabilization, measure the lamp's total power consumption, power factor, total harmonic distortion, and color temperature.
⑤Light Distribution Test:
After the LED street lamp has operated for 1000 hours, apply the rated voltage and input frequency between the input terminals.
Measure the lamp's photometric distribution curve and total light output using a light distribution curve measuring device.
Calculate the lamp's luminous efficiency using the equation: Luminous efficiency of lamps (Im/W) = Total light output of lamps (Im) / Total power consumption of lamps (W).
⑥ Voltage Change Rate Test:
To assess the light distribution characteristics of LED street lamps, measure the central luminous intensity at both 90% and 110% of the rated voltage, maintaining the rated input frequency between the input terminals.
⑦ Temperature Cycle Test:
LED street lights must undergo a temperature cycle test where, in the operational state:
Temperature rises from room temperature to 50°C ± 2°C, remains for 16 hours.
Then, it cools down to -5°C ± 2°C, stays for 16 hours.
Finally, it returns to room temperature, repeating this cycle twice.
The heating and cooling speed should be 0.5~1°C/min.
⑧ Switch Test:
LED street lights are subjected to 1200 switching cycles by applying rated voltage at the rated input frequency between the input terminals, switching on for 30 seconds and off for 30 seconds.
⑨ Durability Test:
After 1000 hours of operation, the LED street lamp should continuously function for 360 hours at an ambient temperature of 60°C±2°C under power. Post-test, after placing the lamp at room temperature for 4 hours, measure its luminous flux. The flux should not be less than 90% of the initial luminous flux.
⑩ Moisture Resistance Switch Test:
Operate the LED street light at an ambient temperature of 40°C ± 2°C and a relative humidity of 90%~98%RH.
Apply the rated voltage at the rated input frequency between the input terminals, switching the lights on for 15 minutes and off for 75 minutes repeatedly for 20 days under these conditions.
⑪ Surge Protection Test:
The test instrument should comply with CNS 14676-5 "Electromagnetic Compatibility Test and Measurement Technology Part 5: Surge Immunity Test".
It should generate a combined waveform of 1.2/50us open circuit voltage and 8/20ps short circuit current.
Apply a test voltage of 4kV, switch electrode polarity, and repeat the test three times.
⑫ Electromagnetic Noise Test:
LED street lights undergo testing following the methods specified in CNS 14115.
⑬ Dustproof and Fireproof Test:
In accordance with CNS 14165 "Electrical Enclosure Protection Classification Level (IP Code)", LED street lights are subjected to testing.
⑭ Wind Tunnel Test:
Expose the lamp to wind level 16 (51.5~56.4 m/s, strong typhoon) for 20 minutes in the direction of maximum projected area.
Inspect the lamp post-test, ensuring no deformation, loosening, falling off, cracking, etc.
⑮ Vibration Test:
Vibrate the lamp in three mutually perpendicular directions.
Inspect for any signs of deformation, loose buckles, falling off, cracks, or other anomalies.
In conclusion, the selection of LED street lights involves a careful consideration of various factors such as lighting methods, industry standards, and performance metrics. Different lighting arrangements suit specific road characteristics, ensuring optimal illumination and coverage. These arrangements vary from single-sided to symmetrical and staggered layouts, with prescribed installation heights and spacing corresponding to distinct light distribution types.
Regarding industry standards, LED street lights demand a focus on safety, thermal testing, photometric measurements, and compliance with specific criteria such as insulation resistance, waterproofing, surge protection, and electromagnetic compatibility. The testing procedures encompass a comprehensive array of assessments, ensuring the durability, performance, and reliability of LED street lights in outdoor environments.
The specifications and testing methodologies outlined provide a comprehensive guide for evaluating LED street lights, encompassing factors like insulation resistance, luminous efficiency, voltage stability, temperature resilience, surge protection, electromagnetic compatibility, dustproofing, fireproofing, wind resistance, and vibration endurance.
In essence, adherence to these standards and methodologies ensures the reliability, durability, and performance of LED street lights, crucial for the safety and efficiency of outdoor lighting solutions in various environmental conditions. Manufacturers, developers, and authorities should prioritize compliance with these rigorous standards to ensure the efficacy and reliability of LED street lighting systems, contributing to safer and well-illuminated urban landscapes.

Contact: Mr. Otis
Phone: +8615815758133
Tel: +8615815758133
Email: Hello@lederlighting.com
Add: No. 1 Gaoxin West Road,High-tech Zone, Jiangmen, Guangdong, China